Immunity is defined as the resistance to infections. The immunity is carried by the disposal of foreign materials. If you want to learn about the immune system, what is the immune system?
If you want to learn about Types of Immunity System, Innate Immunity, Acquired Immunity, Active Immunity, and Passive Immunity, this article is very helpful.
Types of immunity:
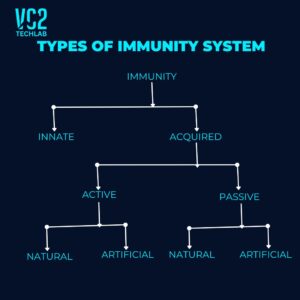
The immune system is differentiated into two types. They are innate immunity and acquired immunity. Acquired Immunity is differentiated into Two Types They are active immunity and passive immunity. Active Immunity is differentiated into Natural Immunity and Artificial Immunity
Innate Immunity : [Innate = Inborn or At birth]
- The means inborn to resistance to infections.
- It is present in all living organisms.
- General protective reactions of organisms against any invasion and not against particular micro organisms is called “non-specific immunity.”
- Physical and mechanical factors.
- Bio-chemical factors.
- Cellular factors—cellular barriors.
- general factors.
- Other factors.
Physical and Mechanical factors
Physical and mechanical factors include:
- Skin
- Mucous Membrane
- Cilia
- Cough and Sneezing
- Peristalasis
Skin:
- It is the First Line of Defense.
- It defends against infections.
- It is to prevent the entry of microorganisms.
Mucous Membrane: The Mucous Membrane Secreates Viscocius Mucous That Traps Entry of Organisms.
Cilia: It is a hair-like structure and swipes out the entry of microorganisms.
Cough and Sneezing: Cough and Sneezing act as driving out the foreign particles.
Bio-Chemicle Factors:
- Secreation of Skin
- Human Milk
- Secration of Gut
- Nosal Secreation
- Lysosomes
- Interferons
- Semen
- Properdin
Secreation of Skin:
- Secreation of Sebaceous and Sweat Glands Act as Antiseptics.
- Which contains lactic acid and fatty acid.
- In the feet, reagion Sebaceous glands are less.
- They have alkali gaps.
- They have a low PH 5.5.
Human Milk:
- Which contain antibacterial substances, namely lactoferrin and neuraminic acid.
- They fight against Ecoil and Staphylococci.
Nasal Secreation: Nasal Secreation Contain mucopolysaccharides, which inactivate certain viruses.
Lysozymes: Tears, Nasal secretion, Saliva, Polymorphenuclear leucocytes, Human Milk, and Most tissue Fluids (Except cerebral Spinal fluids – CSF, Sweat and urine) Contain a mycolytic enzyme, N-acetyle-muramidase, which is lysozyme
Interferons: These are antiviral proteins produced by virus-infected cells and are protecting the neighboring cells from viruses of infected cells. These are 3 types. They are Alpha, Beta and Gamma
Semen: It contains an antimicrobial substance.
Cellular Factors:
Natural immunity is provided by the following cellular factors:
- Phagocytic cells
- Lymphocytes
1. Phagocytosis:
- Phagocytosis is a process of eating cells
(Phago = eating, Cytos = cells) - Discovered by Metchnikoff
- They are of two types:
- Microphages
- Macrophages
- The microphages are nothing but the polymorpho-nuclear leucocytes (PMNLs)
- They include neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
- The monocytes and macrophages constitute the mononuclear phagocytic system or reticulo-endothelial system (RES)
2. Lymphocytes
- Few lymphocytes secrete non-specific cytotoxicity against antigens.
- Natural Killer (NK) cells: cytotoxic
- ADCC (Antibody-Dependent Cytotoxic Cells)
- LAK cells (Lymphokine-Activated Killer Cells)
Acquired Immunity:
The resistance developed by man during his life is known as acquired or adaptive immunity.
The acquired immunity is of two types:
Acquired Immunity
-
Active Immunity
- Natural
- Artificial (Passive)
-
Passive Immunity
- Natural
- Artificial
Active Immunity
- Active immunity is a substance developed in an individual in response to an antigenic substance (antigenic stimulus).
- Active immunity involves:
- The synthesis of specific antibodies (Humoral immunity)
- The production of immunologically active cells (Cell-mediated cells)
Humoral immunity:
The immunity is mediated by the antibodies that are released into the fluids of the body. Such as plasma, lymph etc. is called humoral immunity.
Cell-mediated immunity:
The immunity developed by the sensitized lympho cells is called cell-mediated immunity.
It is two types. ASC (protein)
- Natural active immunity
- Artificial active immunity
1. Natural active immunity:
The resistance developed by an individual in response to a natural infection from which a person recovers is called natural active immunity.
Ex: Small pox, chicken pox, measles
2. Artificial active immunity:
The immunity developed by an individual due to the inoculation of bacterial antigens into the body is called artificial active immunity.
The immunity developed by vaccination.
Live vaccine (attenuated):
In this preparation, live microorganisms are attenuated by different methods.
Passive Immunity
The immunity resistance developed by an organism due to the transfusion of ready-made (performed) antibodies is called passive acquired immunity.
It is two types:
- Natural passive immunity
- Artificial passive immunity
1. Natural passive immunity
If the immunity system is transferred from mother to child.
- Transfer of antibodies from mother to fetus across the placenta or from mother to child through colostrum.
2. Passive artificial passive immunity
If the pre-formed antibodies are transferred from an immunized host to a non-immunized acceptor,.
- Artificial passive immunity is therapeutically used in the treatment of tetanus, diphtheria, gas gangrene, snake bite, and immune deficiency states.
